

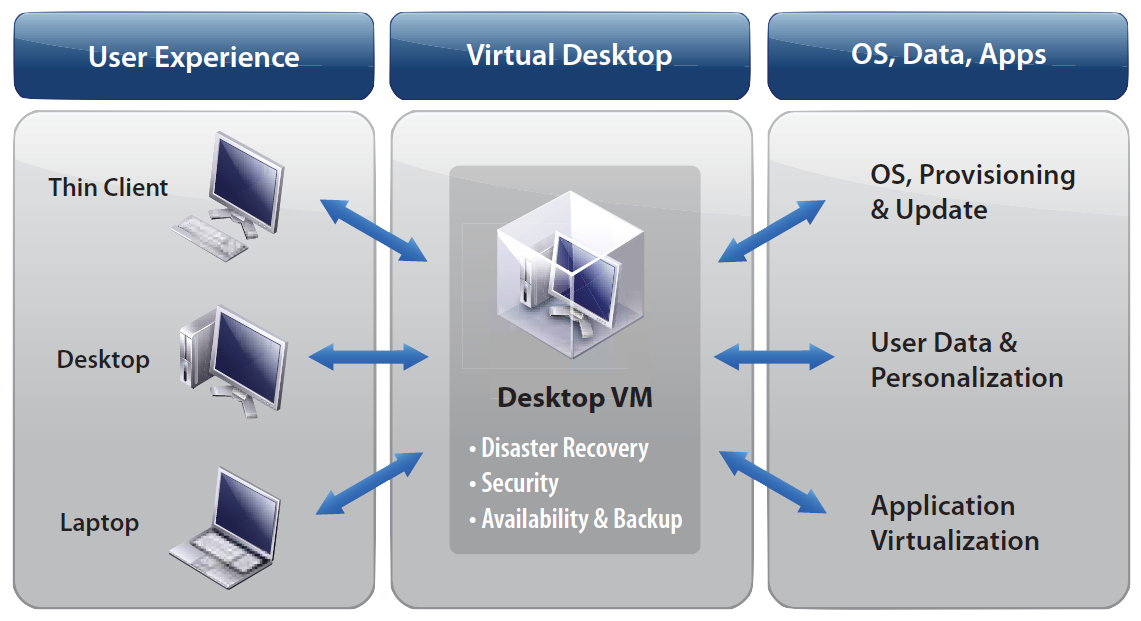
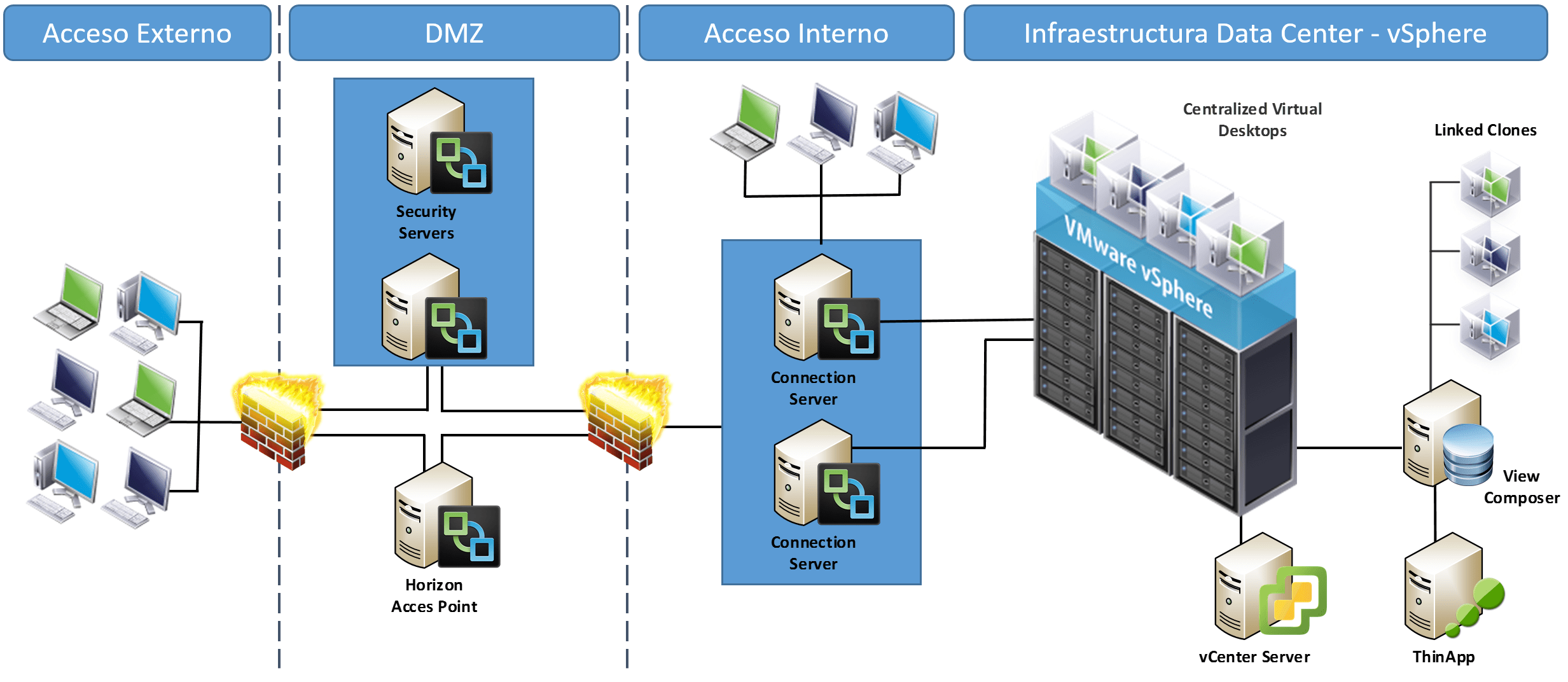
Simplified management is often a benefit of VDI groups of users can share virtual desktops or IT can deploy desktops without much customization. VDI can be cost effective for companies that have a large employee base, particularly if IT can deploy shared or pooled virtual desktops that cut down on the number of overall desktops in the organization. VDI enables users to access full desktop capabilities on thinner machines, as most of the processing and computing happens on the back end. The user must be connected to a network to access the desktop, although some VDI software offers offline capabilities. The user can then interact with the desktop on their endpoint device, whether that's a thin client, mobile device, laptop or other client. With VDI, a desktop OS is hosted on a central server that sends the desktop interface over a remote display protocol. VDI to understand the differences between these two approaches and determine which one is right for their organization. IT admins should compare desktop as a service vs. From a user perspective, these methods are most successful when they provide the same user experience a person would get from a physical, local desktop. Both technologies can help organizations provide business continuity to remote employees and offer the ability to scale up or down quickly as employee bases change. There are multiple ways to implement virtual desktops, including virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) and desktop as a service (DaaS). Desktop virtualization enables IT to deploy a hosted OS to remote clients.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
